Recursion
Introduction:-
Recursion is when a function
calls itself repeatedly until a specific
condition is met. It's like a function that keeps calling itself to solve a problem by breaking
it down into smaller parts. This technique is often used to solve complex
problems by dividing them into simpler sub-problems.
By using recursion, you can
solve various problems , such as finding
the factorial of a number
or generating a Fibonacci series. It's a
powerful concept that allows you to tackle intricate tasks in a more organized
and efficient manner. It can be particularly useful for tasks such as searching
and sorting algorithms, working with complex data structures like trees and
graphs, and solving mathematical problems. It is a clever and efficient way of
solving a complex tasks or problem.
Fundamental of recursion:-
The fundamental of recursion consists
of two objects which are essential for any recursive
function. These are:
1. Recursion case:
The recursion case refers to the recursive
call present in the recursive function. It decides what type of recursion will occur and how the
problem will be divided into smaller sub problems.
2. Base condition:
The base condition
specifies when the recursion is going to terminate. It is the condition that determines the exit point of the
recursion.
Note:
It is important to define the base condition
before the recursive
case otherwise, the base
condition may never encountered and recursion might continue till infinity.
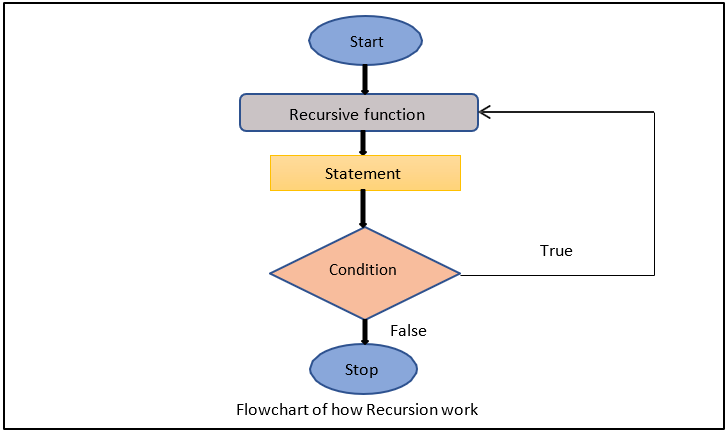
How Recursion work?
When the recursive method is executed, the program first checks the base case.
If the base case is true, the function
returns and stops. But if the base case is false, the program
moves on to the recursive
case. Inside the recursive case, there's a recursive call. This means that the function calls itself from
within its own code. It's like a loop that keeps going until the base case is
met.
Flowchart:
Types of recursion:-
1. Direct recursion :
Direct recursion
is the most common type of recursion, where a function
calls itself directly
within its own body. The
recursive call can occur once or multiple times within the function.
2. Indirect recursion :
Indirect
recursion is an interesting form of recursion where a function calls another
function, which eventually calls the first function
or any other function in the chain,
leading to a cycle of function calls. In other words, the functions are mutually recursive. This type of recursion involves
multiple functions
collaborating to solve a problem.
Example:-
Sum of natural number using recursion:
Output:-
Applications of recursion:-
Recursion is widely used to solve different
kinds of problems
from simple ones like printing
linked lists to being
extensively used in AI. Some of the common uses of recursion are:
·
Tree-Graph Algorithms
·
Mathematical Problems
·
Divide and Conquer
·
Dynamic Programming
·
In Postfix to Infix
Conversion
·
Searching and Sorting Algorithms
Name :- Priya Dilbahadur Ram
Roll No. :- 11





No comments:
Post a Comment